The most important economic, environmental, and developmental problems facing the globe today all revolve around energy. Energy services that are clean, efficient, cost-effective, and dependable are essential for world success. Energy cost reduction and mill operational performance can both be increased with the use of energy management and optimization solutions. Due to the growing worldwide demand for sustainable development, this chapter’s emphasis is on energy-related concerns and covers specific technological solutions. Other subjects will also be covered, such as the most recent developments in sustainable energy for infrastructure and industry, as well as increasing operational effectiveness. Energy Management courses are provided by NTPC school of business. you can join the best course here.
What is Clean Energy?
Clean energy is energy that is fully developed to meet our current needs for environmental preservation and to address the non-renewable fuel dilemma. There are distinctions between clean and renewable energy sources despite having no waste or pollution.
Clean energy is produced by production processes that do not emit any pollutants, particularly greenhouse gases like CO2 that contribute to global warming. In order to improve environmental protection and ease the crisis caused by non-renewable resources like gas and oil, clean energy, which is currently in full growth, is essential.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN CLEAN AND RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES
The terms “clean energy” and “renewable energy” are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing, and it is crucial to recognise this. The pollution they produce is the first distinction. You might not be aware that clean energy sources can pollute.
For instance, biogas and biodiesel are renewable energy sources since they are produced from natural, non-depletable sources. However, they damage the atmosphere through combustion and release greenhouse gases, unlike the majority of renewable energies.
Since clean energies do not cause pollution, it is reasonable to conclude that most renewable energy sources are likewise clean, and vice versa.
THE MOST COMMON TYPES OF CLEAN ENERGY
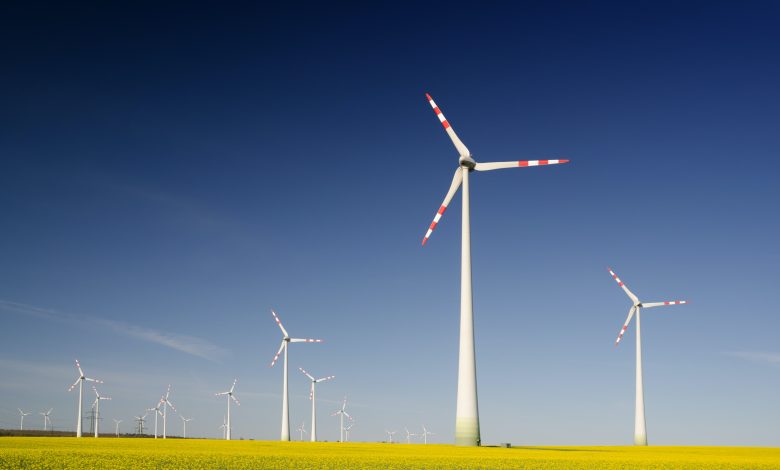
Most Common clean energy is also renewable energy are nuclear energy, wind energy, solar energy, Hydroelectric energy, Geothermal energy, and Tidal energy.
-
Nuclear energy
Contrary to popular belief, nuclear energy is clean during the whole production process and is almost endless when using the present uranium reserves, which will be able to continue producing the same amount of energy for thousands of years.
In actuality, the atmosphere is primarily filled with water vapour from nuclear reactors. There is no room in the calculation for CO2, methane, or any other sort of harmful gas that exacerbates climate change. A single power plant may produce a staggering quantity of energy because to the huge power contained in nuclear energy, which is another important point to remember.
There are two ways to produce this energy: nuclear fusion and fission. When atoms join or fuse to form a bigger nucleus in the first of these processes, energy is released. The second occurs when the nuclei split apart to generate smaller ones, which then release energy.
2. Geothermal energy
Utilizing power stations situated on deposits, it is a type of clean, renewable, and endless energy that captures the heat that the Earth’s core produces. The heat may come from layers of hot water flowing beneath the surface if they are hot water deposits, or it may come from rocks if they are dry deposits.
3. Tidal energy
It uses the energy of the waves to generate electricity in a sustainable, local, and limitless manner.
Other forms of renewable energy include solar thermal energy, which harnesses the heat from the sun, wave energy, which transforms the power of the ocean’s thermal gradient between cooler deep saltwater and warmer shallow or surface water, and ocean thermal energy conversion. In addition to these, a growing number of hybrid energy projects are appearing that combine several renewable energy sources to guarantee a more reliable, effective supply.
4. Hydroelectric energy
Hydroelectric power employs the force of water falling from a height or flowing down a slope to produce electricity. It is a clean, renewable, emission-free, local source of energy. The most effective, extensive form of energy storage now used is hydroelectric pumping stations, which are a subset of this sort of power generation.